
Understanding Diamond Quality
Learn about Carat, Cut, Color, and Clarity—the four key factors that determine a diamond's quality and value.

Carat Weight
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams.
Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its 'points' alone. For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point oh eight carats.'
All else being equal, diamond price increases with diamond carat weight because larger diamonds are more rare and more desirable. But two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different values (and prices) depending on three other factors of the diamond 4Cs: Clarity, Color, and Cut.
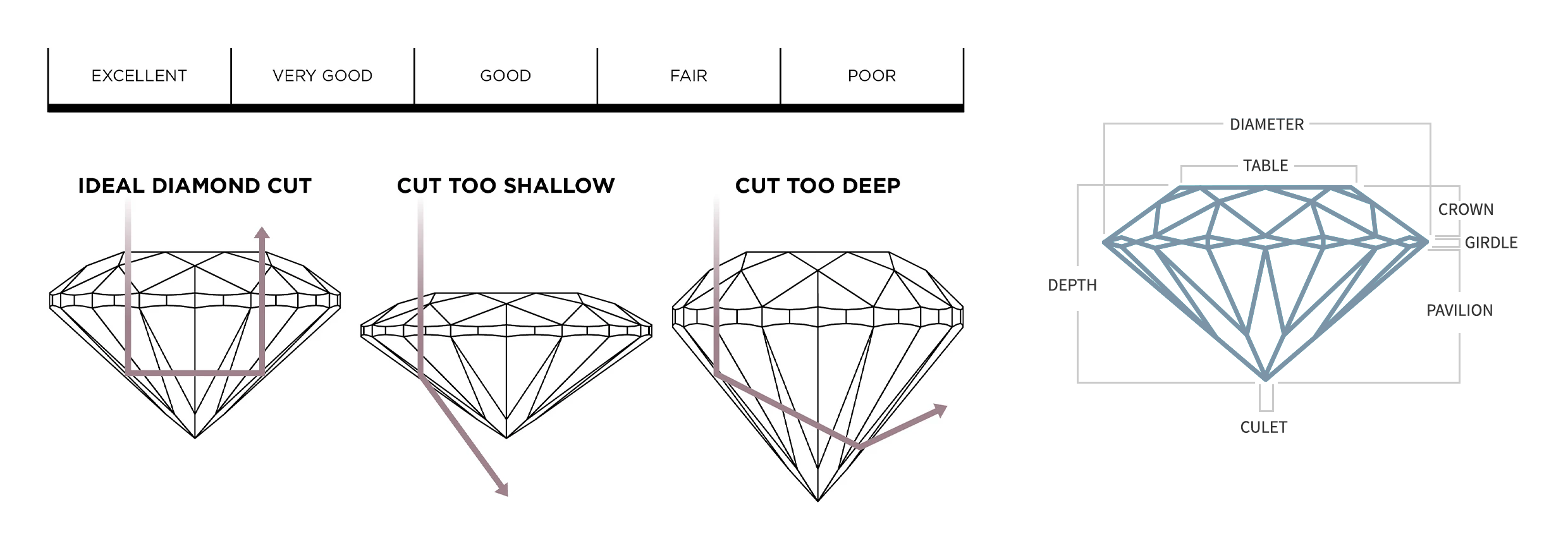
Cut
Cut is the only diamond component not influenced by nature, and it's considered the most important of the 4Cs. This factor refers to the quality of the diamond's cut, not the shape or size (although these can be interchangeable), and how well the stone is faceted, proportioned, and polished. This also determines how the diamond interacts with light.
Brilliance, which is the diamond's ability to return light to the eye, is measured solely by the stone's cut (color and clarity have no impact). For any diamond shape, visually, cut is the first C to consider, followed by color, and, least as important, clarity (as long as the diamond has no visible imperfections).
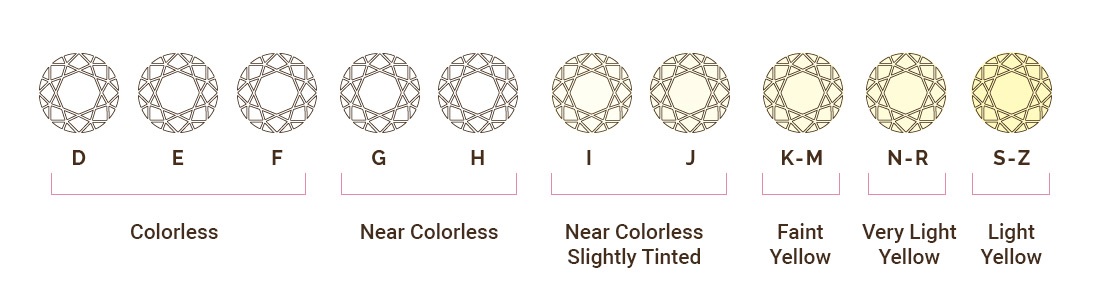
Color
Diamond color is actually the absence of color. Everyone has a different tolerance for how much color they like in a diamond. H and G are near colorless, or a warm white and are the best value for a "colorless" diamond.
F and E are completely colorless and are a pure cool white, these stones in my opinion are the perfect diamond color. D is the rarest and coolest white available, and the most expensive.
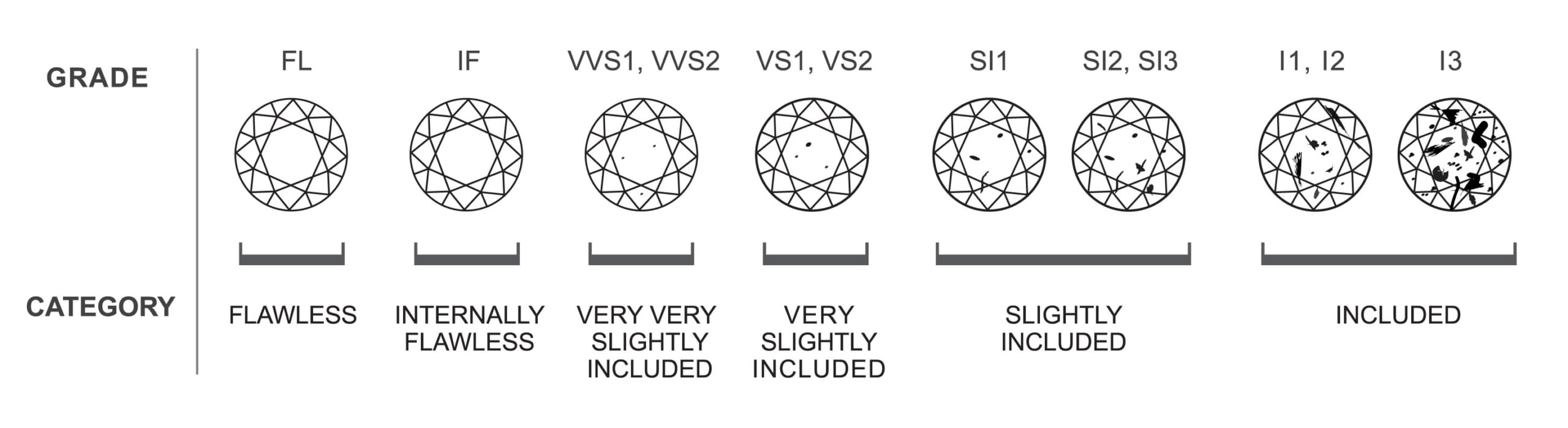
Clarity
Diamonds are stones formed in the earth under extreme pressure. These rocks when forming crack, cloud and spots of uncrystallized carbon can become trapped as black specks. Inclusions are not bad, and MOST diamonds have them in one form or another.
Depending where the inclusions are, how many there are and of what type, they are often invisible to the unaided, untrained eye. Diamond clarity refers to the absence of these inclusions and blemishes. Diamonds without inclusions are very rare and are graded as IF or Internally Flawless.
SI2 and SI1 can be very clean and are the best value. VS diamonds will be more brilliant, and will sell for a higher price than the SI diamonds.
Understanding Diamond Grades
Cut Grades
🔷 Ideal - Maximum light return and brilliance
🔶 Excellent - Exceptional light performance
🔶 Very Good - High-quality appearance
🔷 Good - Noticeable light performance
Color Grades
D, E, F - Colorless (Premium)
G, H, I, J - Near Colorless
K, L, M - Faint Color
N-Z - Light to Fancy Color
Ready to Find Your Perfect Diamond?
Use your knowledge of the 4Cs to explore our collection and find the perfect stone.